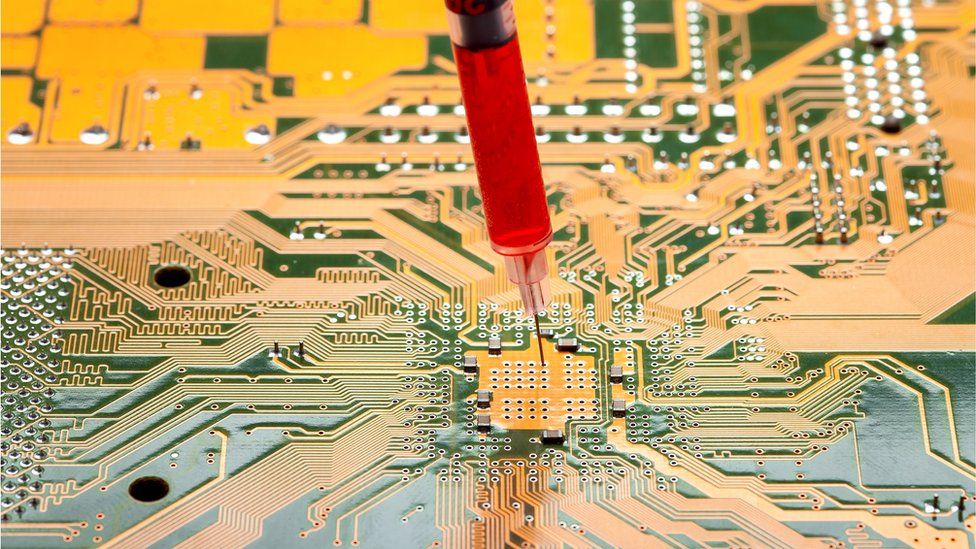
There are already a number of companies in China offering genetic tests direct to consumers. Investors are betting big on Genebox, which offers unbelievably low prices, and plans to develop critical technology locally.
If you give Genebox a tube of spit and as little as $3, the company promises to tell you the best strategy for you to lose weight and care for your skin, your risks of developing diabetes or cancer, and who your ancestors are. The Beijing-based startup is one of the over 100 companies in China’s direct-to-consumer DNA test industry, which is expected to see $405 million in sales by 2022.
Genebox announced (in Chinese) this Monday that it had raised “tens of millions in U.S. dollars” in a Series A+ round of financing led by Centurium Capital.
- Founded in 2018, Genebox previously netted around 136 million yuan ($21 million) in its angel round led by the leading drug retail chain Dashenlin Pharmaceutical, and the Series A led by the consumer- and healthcare-focused Centurium Capital.
Genetics is a core focus of China’s push to become a global leader in healthcare, science, and technology. With government encouragement, direct-to-consumer DNA-testing companies like Genebox and its domestic rival, 23Mofang, provide extremely affordable and accessible gene analysis services.
- As of 2019, more than 2.2 million Chinese had sent test tubes of spit to private companies to have their DNA analyzed. The number has surged since 2017, when the National Development and Reform Commission listed genetic testing in the 13th Five-Year-Plan’s strategy for the biological industry, according to Shenzhen-based Qianzhan Industry Research Institute (in Chinese).
- While most DNA tests are conducted through healthcare providers for medical purposes, direct-to-consumer genetic testing is typically marketed directly to younger consumers through the internet and social media, with the selling points being historical information about ancestry and predictions about future health.
Chinese genetic testers offer almost unbelievably low prices
Chengdu-based 23Mofang was one of the first direct-to-consumer genetic testing startups in China, founded in 2015 after the founder, Zhōu Kūn 周坤, was inspired by America’s 23andMe and supported by cash infusions from six rounds of fundraising totaling 160 million yuan ($24.5 million).
- By 2017, 23Mofang had brought the price of DNA testing down to 499 yuan ($76), one-fourth of the cost from other providers when the service debuted in the Chinese market in 2013.
- Genebox entered the market in 2018 and took the starting price even lower, to 19.9 yuan ($3). Lǐ Zhì 李智, Genebox’s founder and CEO, said the company attempts to attract users to send their DNA samples through the low basic package price, and they can pay additional fees to unlock other data and analysis.
- GeneBox only ships test kits to mainland China addresses, while 23Mofang said it also serves overseas Chinese nationals. In the U.S., 23andMe’s basic test is currently selling for $79. The American company ships to Hong Kong, but does not offer services for mainland China residents.
To localize the genetic testing procedure and further lower costs, Genebox earlier this year announced (in Chinese) it had made China’s first independently developed microarray, a biochip that measures the expression levels of a large number of genes at the same time, breaking into the upstream technology market currently dominated by America’s Illumina.
- Li said Genebox is mass-producing the new biochips and aims to replace all imported microarrays by next spring.
Privacy concerns are rising as direct-to-consumer genetic testing companies gain more popularity in China.
- Genebox says in the terms of service that it will not share any personal information with third parties without user consent, but exceptions include complying with certain laws and regulations or if “forcefully” required by the government.
- Beijing retains the right to access data held by all Chinese companies for national security, public health, and social interest reasons, according to China’s Personal Information Security Specification.
- Genebox said it may also share user data with its subsidiaries, affiliated organizations, or third-party research institutions for purposes such as scientific and medical research, as well as new product development. 23Mofang has an even longer list of scenarios where it may use genetic data without consent, including news reporting and system maintenance.
- Both Genebox and 23Mofang said they will eliminate personal identity information from the data before sharing it with third parties for research purposes. “Personal information after anonymization is not personal information,” 23Mofang says in its terms of service (in Chinese). “23Mofang has the right to mine, analyze, and utilize the anonymized user database.”